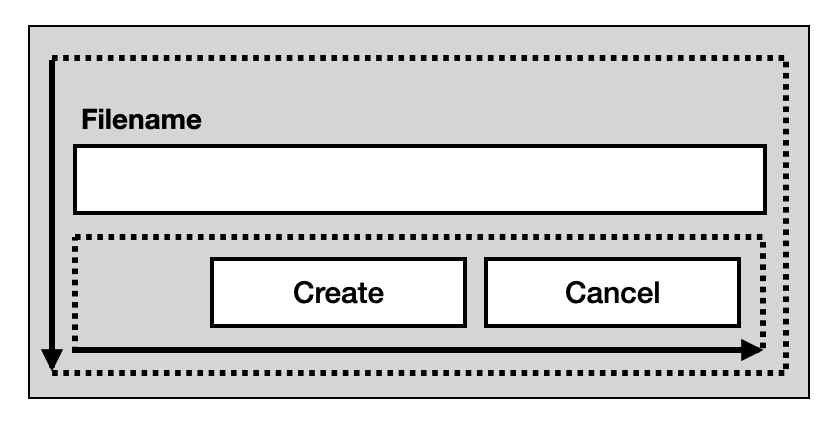
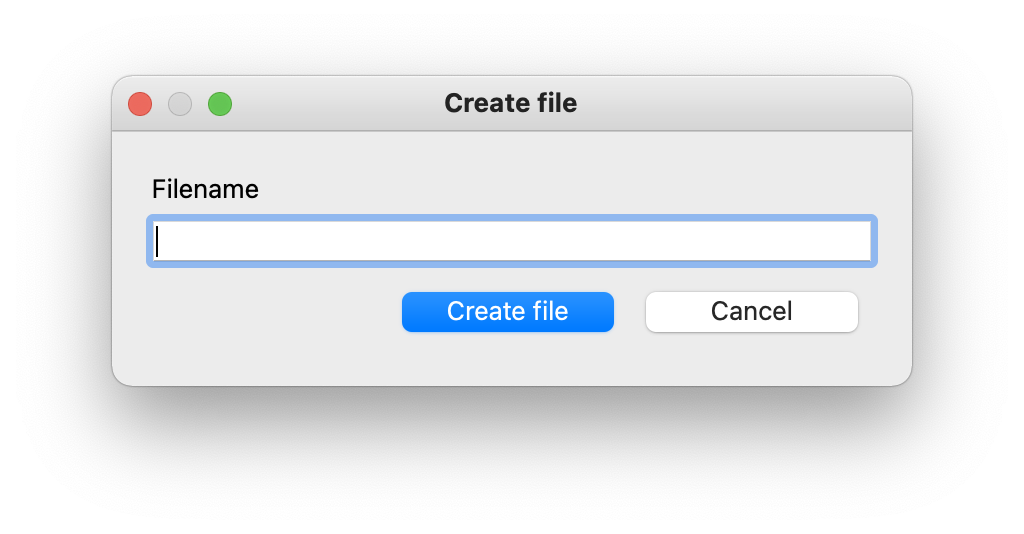
This is what you will build with pyside:
I’m going to use pyside6 with the features snake_case and true property
syntax enabled by importing: from __feature__ import snake_case,
true_property
Here is the full code to show the Dialog with two nested box layouts:
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QVBoxLayout
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QHBoxLayout
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QDialog
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QLabel
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QPushButton
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QLineEdit
from __feature__ import snake_case, true_property
class CreateDialog(QDialog):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.window_title = "Create file"
verticalbox = QVBoxLayout()
verticalbox.add_widget(QLabel("Filename"))
verticalbox.add_widget(QLineEdit())
horizontalbox = QHBoxLayout()
horizontalbox.add_stretch() # aligns other box contents to the right
button1 = QPushButton("Create file")
button1.set_fixed_width(120)
horizontalbox.add_widget(button1)
button2 = QPushButton("Cancel")
button2.set_fixed_width(120)
horizontalbox.add_widget(button2)
verticalbox.add_layout(horizontalbox)
verticalbox.add_stretch() # aligns other box contents to the top
self.set_layout(verticalbox)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
dialog = CreateDialog()
dialog.show()
app.exec_()
And here is the result:
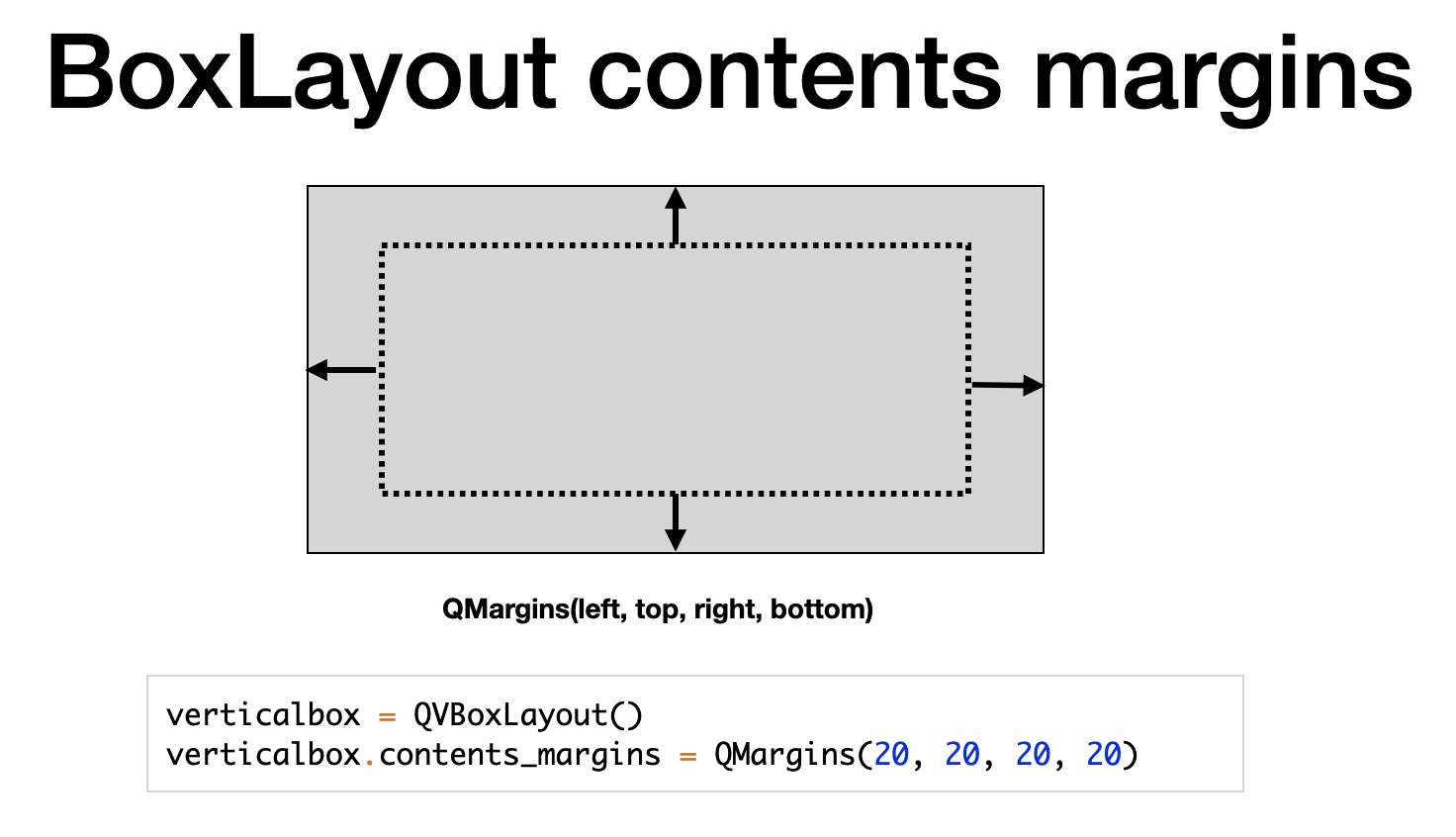
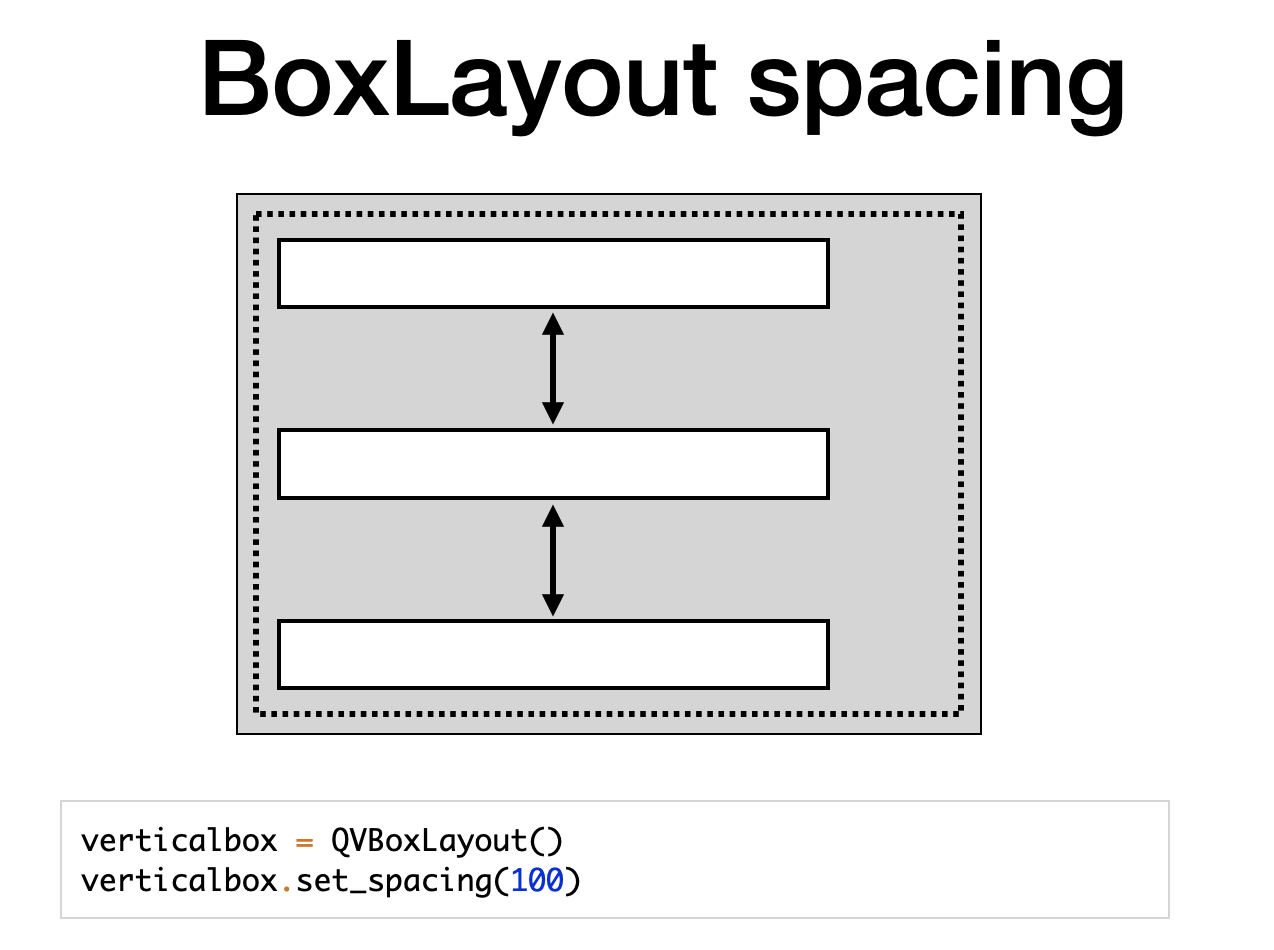
If you want more control over the contents in box layouts, you can use the contents_margins property and set_spacing method.
Here are two slides from my Python training where I teach how to build graphical user interfaces with Python and Qt: